Quantum Mechanics Simplified
Breaking down the complex world of quantum mechanics into simple concepts for everyone.
Introduction
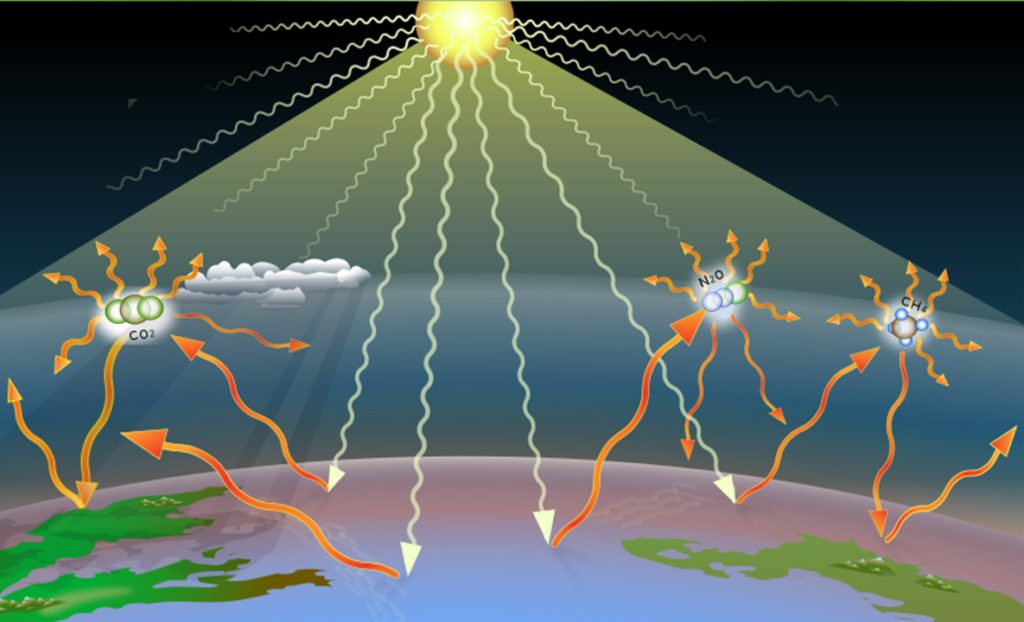
Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that studies the behavior of matter and energy at the smallest
scales—atoms and subatomic particles. Its principles often defy our everyday experiences, introducing
concepts like wave-particle duality, quantum superposition, and entanglement. Despite its complexity,
quantum mechanics forms the foundation of modern technologies such as semiconductors, lasers, and quantum
computers.
Pro Tip: Watch beginner-friendly videos on quantum mechanics to build your understanding step by step.
Wave-Particle Duality
Wave-particle duality is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics, describing how particles like electrons
and photons can behave as both waves and particles. This duality was famously demonstrated in the
double-slit experiment, where light and electrons created interference patterns, revealing their wave-like
nature.
Pro Tip: Experiment with simulations of the double-slit experiment to visualize this phenomenon.
Quantum Superposition
Superposition is the principle that a quantum system can exist in multiple states simultaneously until it is
measured. For instance, an electron can be in different energy levels at the same time. This concept is
central to quantum computing, where qubits can represent multiple states at once, enabling immense
computational power.
Pro Tip: Explore how quantum superposition is utilized in quantum computing to revolutionize data
processing.
Quantum Entanglement
Quantum entanglement describes a phenomenon where two particles become interconnected, such that the state
of one instantly affects the state of the other, no matter the distance between them. Albert Einstein
famously referred to this as "spooky action at a distance." Entanglement plays a key role in quantum
cryptography and secure communications.
Pro Tip: Research real-world applications of quantum entanglement, such as in secure quantum key
distribution.
Applications of Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics underpins many modern technologies, including transistors, MRI machines, and quantum
computers. Ongoing research promises advancements in fields like quantum computing, cryptography, and
teleportation, which could transform industries and solve previously intractable problems.
Pro Tip: Follow companies like IBM and Google to learn about the latest breakthroughs in quantum
technologies.